Top 10 Industrial Valves Every Engineer Should Know About
In the realm of engineering and industrial operations, understanding the various types of industrial valves is crucial for ensuring the efficiency and safety of fluid control systems. Industrial valves are essential components used across a multitude of applications, ranging from water treatment plants to oil refineries. Their primary function is to control, regulate, or direct the flow of liquids and gases, making them indispensable in any industrial process.
As engineers tackle complex projects, having a profound knowledge of the different types of industrial valves is not just beneficial but necessary. Each valve type comes with unique features and functions, tailored to specific requirements and conditions. From gate valves that provide seamless flow when fully open to check valves that prevent backflow, the diversity of industrial valves can significantly impact operational effectiveness. This article presents the top 10 industrial valves that every engineer should know about, offering insights into their characteristics, advantages, and applications to help professionals make informed decisions in their projects.
Fundamental Types of Industrial Valves and Their Applications
Industrial valves are essential components in various engineering applications, playing a crucial role in controlling fluid flow in systems across diverse industries. The fundamental types of industrial valves include gate, globe, ball, butterfly, check, and safety valves, each designed to meet specific operational requirements. For instance, gate valves are often used in on/off services with low flow resistance, making them suitable for applications where full flow is needed. Conversely, globe valves are preferred for throttling services due to their ability to regulate flow effectively.
Butterfly valves, known for their lightweight and compact design, are widely used in large pipelines where quick shut-off is essential. Ball valves enable tight sealing and rapid operation, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent on-off control. Check valves, on the other hand, are crucial for preventing backflow in piping systems, thus safeguarding equipment from potential damage. Lastly, safety valves are indispensable in protecting pressure vessels and piping against pressure fluctuations, ensuring safe operation in industrial processes. Understanding these fundamental types and their specific applications is vital for engineers to select the appropriate valve for their systems, thus enhancing efficiency and safety in various industrial operations.
Key Features and Mechanisms of Each Valve Type
When it comes to industrial valves, understanding their key features and mechanisms is essential for engineers in various sectors. The most common types include
gate, globe, ball, and butterfly valves, each designed for specific applications. For instance,
gate valves are celebrated for their low-pressure drop and tight shut-off capabilities,
making them ideal for on/off service in pipelines. In contrast,
globe valves provide excellent throttling capabilities due to their high flow resistance,
suitable for applications that require flow regulation. According to a report by the Global Industrial Valve Market,
the demand for these valve types is expected to grow by 5% annually due to increasing infrastructure development.
Ball valves, known for their quick operation and minimal pressure drop, are essential in processes requiring fast switching.
Their mechanism allows for a sphere to rotate within the valve body, providing a reliable seal when closed.
Butterfly valves, with their disc design, offer a lightweight and space-efficient solution for modulating flow;
they excel in large-scale applications where space and weight are critical factors.
Industry analyses suggest that the global butterfly valve market is projected to reach
$5.61 billion by 2026, indicating a trend toward more efficient valve systems.
Tips: When selecting a valve, engineers should consider factors such as
pressure rating, temperature, and compatibility with the fluids being handled.
Additionally, familiarity with standard valve symbols and designations can greatly enhance communication within engineering teams and streamline project workflows.
Understanding the nuances of each valve type not only aids in choosing the right solution but also
contributes to long-term operational efficiency.
Material Selection and Durability Considerations for Industrial Valves
When selecting materials for industrial valves, engineers must consider various factors that directly impact durability and performance. The choice of material is crucial as it affects the valve's ability to withstand the operating environment, including temperature, pressure, and corrosion potential. Common materials include stainless steel, cast iron, and plastics, each offering distinct advantages and limitations. For instance, stainless steel valves are well-suited for high-temperature and high-pressure applications due to their strength and resistance to corrosion. In contrast, plastic valves might be preferred in less demanding environments where chemical resistance is critical.
Durability considerations also extend to the valve's design and the specific application it serves. Engineers should assess the valve's operating conditions, such as fluid type and flow rates, to select a material that can endure the stress over time without failure. Additionally, factors like maintenance requirements and the potential for wear and tear under cyclic loading should influence material selection. A well-chosen material not only enhances the lifespan of the valve but also minimizes the need for frequent repairs or replacements, leading to more reliable and efficient operations in industrial settings.
Performance Standards and Testing Methods Relevant to Valves
When it comes to industrial valves, understanding performance standards and testing methods is critical for engineers. These standards dictate the operational reliability and safety of valves in various applications. Common performance standards include ANSI, API, and ASME, each providing guidelines for pressure ratings, temperature ranges, and material specifications. Engineers must familiarize themselves with these norms to ensure that the chosen valves meet operational requirements and industry regulations.
Testing methods play a vital role in guaranteeing that valves function correctly under expected conditions. Common tests include hydrostatic testing, which verifies the valve’s ability to withstand pressure, and cryogenic testing, which assesses functionality at extremely low temperatures. Another important method is the functional test, where valves are put through real-world operation scenarios to confirm their performance. It is essential for engineers to understand these testing methods for selecting the right valve for their projects.
**Tips:** Always check the latest performance standards and testing methodologies before purchasing valves. Engage with suppliers who offer detailed certification reports. Additionally, consider pre-purchase testing to validate performance in your specific application environment, as this can save time and costs in the long run.
| Valve Type | Performance Standard | Testing Method | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Valve | API 608 | Hydraulic Testing | Water, Oil, Gas |
| Gate Valve | API 600 | Shell Testing | Oil & Gas, Water Supply |
| Globe Valve | API 602 | Seat Leakage Testing | Flow Regulation |
| Check Valve | API 594 | Functional Testing | Prevent Backflow |
| Butterfly Valve | API 609 | Performance Testing | HVAC, Water Treatment |
| Pressure Relief Valve | API 520 | Pop Test | Safety Systems |
| Solenoid Valve | ISO 3411 | Electrical Testing | Automation Systems |
| Pinch Valve | API 609 | Leak Testing | Slurry Transport |
| Diaphragm Valve | ISO 15848 | Seat Leak Test | Food, Pharmaceutical |
| Actuated Valve | ISO 9001 | Cycle Testing | Automotive, Industrial |
Emerging Trends in Valve Technology and Innovations
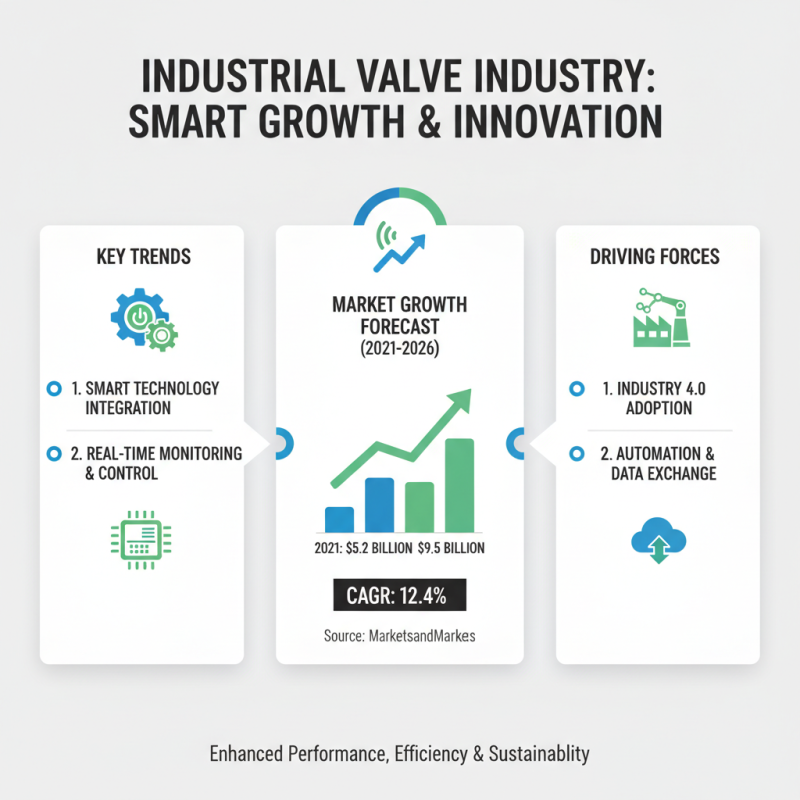
In recent years, the industrial valve industry has experienced significant advancements driven by the need for enhanced performance, efficiency, and sustainability. Key trends include the integration of smart technology, which allows for real-time monitoring and control of valve operations. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global smart valves market is expected to grow from $5.2 billion in 2021 to $9.5 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.4%. This growth is largely attributed to the increasing adoption of Industry 4.0 practices, which emphasize automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies.
Another emerging trend is the focus on environmentally friendly materials and designs. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint, there has been a shift towards using sustainable materials such as recycled metals and engineered plastics. Additionally, innovations in valve design, such as zero-leakage technologies, are becoming more prevalent. According to a study published by the International Society of Automation, approximately 15% of industrial valve failures are due to leakage, leading to unplanned downtime and increased operational costs. Thus, the introduction of advanced sealing technologies is critical in enhancing reliability and minimizing environmental impacts. As these trends continue to evolve, engineers must stay informed about the latest technological advancements to optimize their systems effectively.
Related Posts
-

Exploring the Future of Industrial Valves: Innovations and Trends Shaping the Industry
-
Understanding the Essential Role of Trunnion Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Trunnion Valve for Your System
-

The Essential Guide to Choosing the Right Floating Valve for Your Water Systems
-

What is a Stainless Steel Globe Valve and Its Key Benefits for Industries
-
Unlocking the Benefits of Carbon Steel Ball Valves: A Comprehensive Guide to Selection and Usage
