Top Floating Valve Types for Efficient Fluid Control?
Floating valves play a crucial role in effective fluid control systems across various industries. According to a recent market analysis report by TechSci Research, the global floating valve market is projected to reach $10 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.5%. This demand underscores their importance in various applications, including water treatment and manufacturing.
John Smith, a leading expert in fluid dynamics, states, "The right floating valve can significantly enhance system efficiency." This highlights the need for engineers to choose the most suitable valve type for their specific applications. Despite the benefits, many still struggle to understand which valve types provide optimal performance.
Choosing the correct floating valve requires insight and precision. Some solutions may not suit all scenarios, leading to inefficiencies. It's crucial to recognize that not all floating valves are created equal. Misunderstandings in selection can result in operational issues. Getting this right requires reflection and understanding of specific system requirements.

Overview of Floating Valve Functionality in Fluid Control
Floating valves play a crucial role in fluid control systems. Their primary function is to maintain fluid levels in various applications. These valves float on the liquid surface and respond to changes in fluid levels automatically. When the level rises or falls, the valve opens or closes accordingly. This operation helps in preventing overflow or dry conditions.
Choosing the right type of floating valve can be challenging. Different designs suit various applications. For instance, some are better for water systems, while others work well with oil. Understanding your specific needs is vital for optimal performance.
Tips: Regular maintenance is essential to keep the valve functioning well. Check for any signs of wear or corrosion. Ensure the float moves freely. Sometimes, a simple cleaning can improve performance significantly. Don't overlook small issues, as they can lead to larger problems. Consistency is key in fluid control efficiency.
Types of Floating Valves: A Comparative Analysis of Designs
Floating valves are essential for managing fluid flow. Their designs vary, impacting efficiency and reliability. Understanding these variations is crucial for effective fluid control in various applications.
Common types include ball valves, flapper valves, and diaphragm valves. Ball valves offer quick shut-off, but may leak if worn. Flapper valves are simple but can fail in heavy flow conditions. Diaphragm valves provide good sealing, yet they may require frequent maintenance. Each design presents unique advantages and challenges.
Consider the working environment before choosing a valve type. Factors like temperature and fluid viscosity play a role. Some designs might not perform well under specific conditions. Experimenting with various styles can yield valuable insights. The goal is to maximize efficiency while minimizing risks.
Applications of Floating Valves in Various Industries
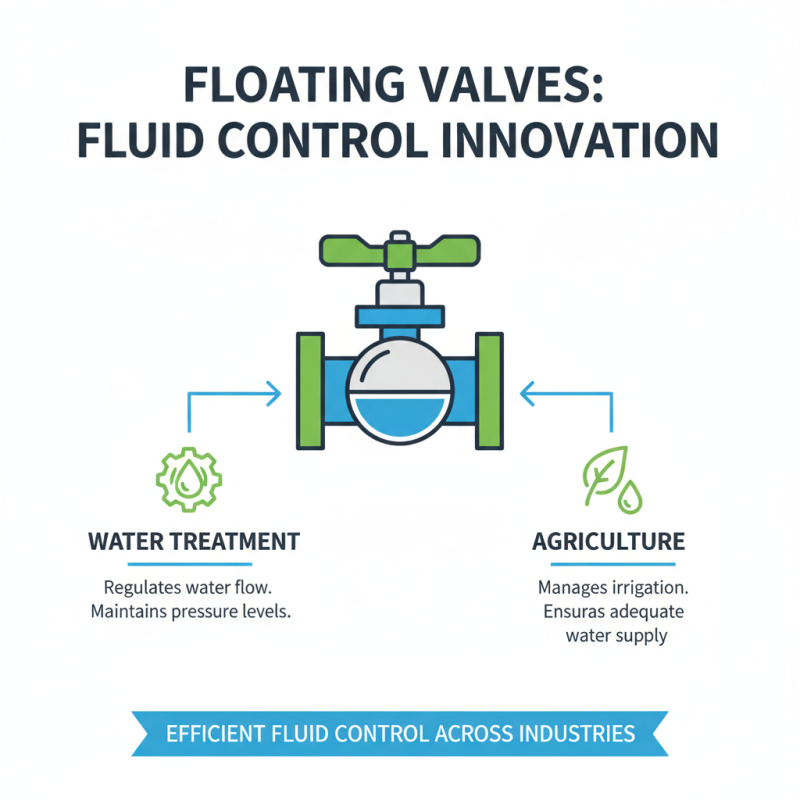
Floating valves play a crucial role in various industries, enabling efficient fluid control. They are often used in water treatment facilities. Here, they regulate water flow to maintain pressure levels. In agriculture, floating valves help manage irrigation. This ensures that crops receive adequate water supply.
In chemical processing, floating valves are vital too. They prevent backflow and maintain safety. Ineffective valves can lead to leaks, posing risks. The food and beverage industry also relies on these valves. They ensure hygiene and control in distribution systems. However, not all installations are perfect. Some may require regular maintenance to function optimally.
Every industry faces unique challenges. Valve sizes and types may not fit as expected. Selecting the right floating valve can be complex. It requires careful consideration of materials and fluid properties. Real-world applications often highlight the need for improvements. Addressing these issues can enhance efficiency and safety significantly.
Advantages of Using Floating Valves for Fluid Management
Floating valves play a crucial role in fluid management. Their design provides significant advantages for efficient control of liquids. These valves float on the surface of the liquid. This allows for accurate adjustments without complex mechanisms. They respond effectively to changes in pressure and flow.
One key benefit is their reduced energy consumption. They operate on simple principles, making them cost-effective. Users can expect lower operational costs. Another advantage is their adaptability. Floating valves can be used in various applications, from ponds to industrial systems.
Tips for using floating valves include regular inspections. Check for wear and tear that may affect performance. Proper maintenance ensures longevity and effectiveness. Make sure the environment is suitable for the valve material. Each application might require different specifications. Experimentation may reveal insights into optimal usage, but don't hesitate to reevaluate your choices. The right valve can transform fluid management efficiency.
Maintenance Practices for Optimal Floating Valve Performance
Floating valves play a crucial role in fluid control systems. Regular maintenance ensures they perform efficiently. Begin by inspecting the valve regularly. Look for signs of wear or damage on seals and seats. Small leaks or unusual noises can indicate issues. It's best to address these problems early.
Cleaning is equally essential. Remove any debris or buildup around the valve. This prevents blockages and promotes smooth operation. Use appropriate cleaning solutions to avoid causing any damage. After cleaning, inspect the valve's movement. It should glide freely without resistance. If you notice sticking, it’s time to assess your maintenance routine.
Don't overlook lubrication. Greasing the moving parts helps maintain function. However, be cautious; too much grease can attract dirt. Always refer to guidelines for proper lubrication amounts. Regularly testing the valve’s performance is vital. This helps you spot any anomalies before they cause major failures. It’s not just about fixing; it’s about ongoing evaluation.
Top Floating Valve Types for Efficient Fluid Control
Related Posts
-

Exploring the Future of Industrial Valves: Innovations and Trends Shaping the Industry
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Trunnion Valve for Your System
-
Top 10 Industrial Valves Every Engineer Should Know About
-

10 Best Ball and Globe Valves for Optimal Fluid Control in Industrial Applications
-

The Essential Guide to Choosing the Right Floating Valve for Your Water Systems
-

Top 10 Ball Valves for Industrial Applications You Should Consider
