Top 10 Ball Valves You Need to Know for Your Next Project
In the realm of industrial applications, ball valves stand out as a crucial component for managing the flow of fluids in various systems. According to industry expert John Smith, a recognized authority in valve technology, “The efficiency of a system often hinges on the choice of valves, and ball valves provide an unmatched combination of speed, reliability, and durability.” As we explore the top 10 ball valves you need to know for your next project, it becomes evident that understanding the different types, materials, and functionalities of these valves is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring safety.
Whether it's for water treatment facilities, oil and gas installations, or HVAC systems, ball valves are pivotal in regulating flow and pressure. Their simple yet effective design allows for quick opening and closing, making them ideal for applications where time is of the essence. The adaptability of ball valves to various environments further underscores their importance in modern engineering. By delving into the leading options available on the market, professionals can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and longevity in their projects.

Overview of Ball Valves and Their Applications
Ball valves are essential components in various industrial applications, renowned for their reliability and durability. Typically characterized by a spherical disc, these valves control the flow of liquids and gases through a system. Their design allows for quick operation, as they can be fully opened or closed with just a quarter turn of the handle. According to the Market Research Future report, the global ball valve market is projected to reach approximately $16 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand across several sectors, including oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing.
The versatility of ball valves extends to a wide range of applications. In the oil and gas industry, they are employed in pipeline systems to ensure efficient flow control under high pressure and high temperature conditions. A report by Fortune Business Insights notes that the rising investments in oil and gas infrastructure are bolstering the use of ball valves in exploration and production activities. Additionally, in the water treatment sector, ball valves play a critical role in managing water flow, ensuring safety and efficiency in treatment plants. The American Water Works Association emphasizes that the use of high-quality valves can substantially reduce maintenance costs and enhance system performance, further highlighting their importance in modern infrastructure projects.
Top 10 Ball Valves You Need to Know for Your Next Project
This chart illustrates the top 10 types of ball valves commonly used in various industrial applications, showcasing their respective flow coefficients (Cv) which indicate how well they can control the flow of fluid.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing a Ball Valve
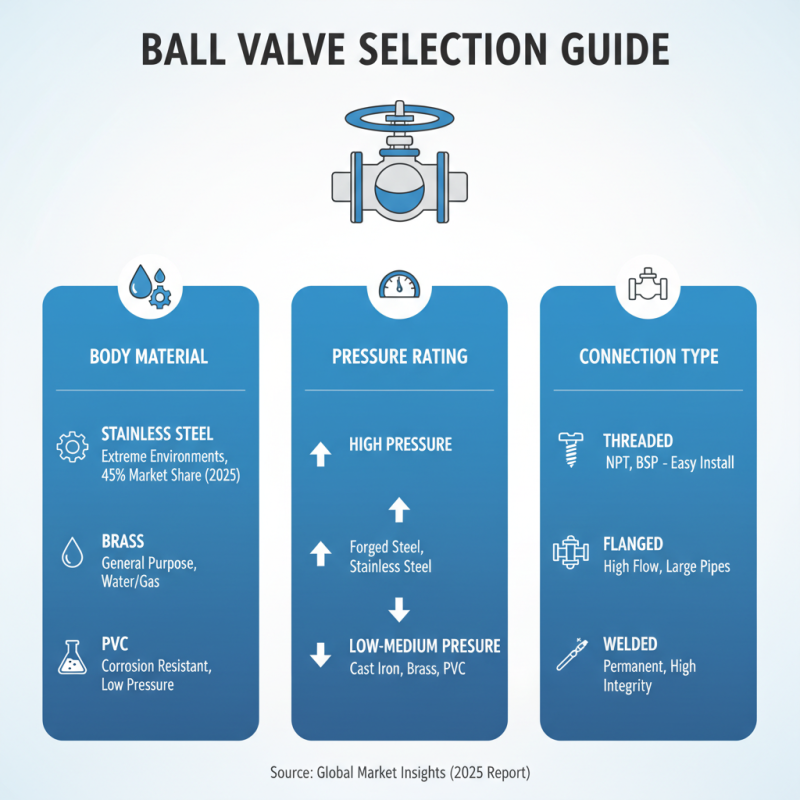
When selecting a ball valve for your next project, several key features should be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability. One of the primary factors is the valve's body material. Common materials include stainless steel, brass, and PVC, each serving specific applications based on pressure ratings and corrosion resistance. According to a report by Global Market Insights, stainless steel valves are expected to dominate the market due to their robustness in extreme environments, accounting for approximately 45% of the total market share by 2025.
Another critical consideration is the valve size and connection type. Ball valves are available in various sizes, typically between 1/4 inch to 12 inches, and the choice of connection—whether threaded, flanged, or welded—can affect installation and compatibility with existing systems. Industry analysis has indicated that mismatched sizes and connection types can lead to inefficiencies, emphasizing the need for precise fitting. Furthermore, understanding the flow coefficient (Cv) of a ball valve is essential, as it determines the flow capacity and influences the energy efficiency of the entire system. Reports highlight that inefficient valve selections can result in significant pressure drops, thereby impacting operational costs and system performance over time.
Top 10 Ball Valves: Specifications and Unique Benefits
When selecting ball valves for your next project, understanding their specifications and unique benefits is crucial. Ball valves are renowned for their ability to provide a tight seal and excellent flow control. Typically made from robust materials like stainless steel or brass, they are well-suited for a variety of applications, including water, gas, and chemical services. The key specifications to consider include port size, pressure rating, and temperature range, which all play a significant role in determining the valve's suitability for specific operational conditions.
In addition to standard specifications, each type of ball valve offers unique advantages. For example, some valves feature a full-port design that minimizes pressure drops and allows for higher flow rates, making them ideal for applications requiring maximum efficiency. Others, equipped with special coatings or seals, provide enhanced corrosion resistance, extending their lifespan in harsh environments. Additionally, automated options are available that integrate seamlessly with control systems, offering precise operation and reducing manual intervention. By carefully evaluating these specifications and benefits, you can select the ideal ball valve that meets the demands of your project.
Maintenance Tips for Ensuring Optimal Ball Valve Performance
Maintaining optimal performance of ball valves is crucial for ensuring the efficiency and safety of your piping systems. Regular maintenance not only prolongs the lifespan of these components but also prevents costly downtime. According to industry reports, nearly 30% of valve failures can be attributed to improper maintenance practices. To avoid these pitfalls, it’s essential to incorporate a structured maintenance plan that includes regular inspections and timely repairs.
One effective tip is to perform routine visual and operational checks. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or leakage, as these can indicate a potential failure. Additionally, regular cycling of the ball valve can help keep the mechanics in good condition. A study by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) suggests that valves should be exercised at least once a month to avoid sticking or seizing. This practice ensures smooth operation and reduces the risk of unforeseen failures during critical operations.
Another important maintenance tip is to monitor the valve’s environment. Excessive heat, pressure, or corrosive substances can significantly affect performance and longevity. Implementing protective measures, such as thermal insulation or chemical inhibitors, can mitigate these risks. A report from the Valve Manufacturers Association indicates that implementing such preventative strategies can increase valve reliability by up to 40%. By following these maintenance tips, you can help ensure that your ball valves operate at peak efficiency throughout their service life.
Comparative Analysis of Ball Valve Materials and Durability
When selecting ball valves for industrial applications, understanding the materials and their durability is crucial. Ball valves are commonly made from various materials such as stainless steel, brass, plastic, and carbon steel, each offering different characteristics that influence their performance across different environments. Stainless steel provides excellent corrosion resistance and is suitable for high-pressure applications, while brass is favored for its excellent thermal conductivity and ease of machining. Plastic valves are lightweight and resistant to certain chemicals, making them ideal for less demanding applications.
Durability is a key factor to consider when evaluating the right ball valve for your project. The choice of material directly impacts the valve's lifespan and ability to withstand environmental stresses, such as temperature fluctuations and exposure to corrosive substances. For instance, valves made from carbon steel are highly durable but can rust if not properly coated or maintained. On the other hand, while plastic valves may lack the strength of metal counterparts, they offer exceptional resistance to aggressive chemical environments. Therefore, a thorough comparative analysis of these materials not only helps in selecting the right valve for specific applications but also ensures reliability and longevity, ultimately contributing to the success of any project.
Top 10 Ball Valves You Need to Know for Your Next Project
| Valve Type | Material | Max Pressure (psi) | Temperature Range (°F) | Durability Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Floating Ball Valve | Brass | 4000 | -20 to 250 | High |
| Trunnion Ball Valve | Carbon Steel | 6000 | -40 to 350 | Very High |
| Full Port Ball Valve | Stainless Steel | 3000 | -40 to 400 | High |
| Reduced Port Ball Valve | Brass | 2500 | -20 to 150 | Medium |
| Electric Ball Valve | Stainless Steel | 1500 | -20 to 300 | High |
| Pneumatic Ball Valve | Aluminium | 2000 | -5 to 250 | Medium |
| High Performance Ball Valve | Chromoly Steel | 4500 | -40 to 450 | Very High |
| Cryogenic Ball Valve | Stainless Steel | 3600 | -325 to 150 | High |
| Swing Ball Valve | Cast Iron | 2000 | -20 to 220 | Medium |
| Diverting Ball Valve | Polymer | 1500 | -40 to 180 | Low |
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Benefits of Using Ball Check Valves in Fluid Control Systems
-

Top 10 Ball Valves for Industrial Applications You Should Consider
-
Unlocking the Benefits of Carbon Steel Ball Valves: A Comprehensive Guide to Selection and Usage
-

Exploring the Future of Industrial Valves: Innovations and Trends Shaping the Industry
-
Understanding the Essential Role of Trunnion Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-

The Essential Guide to Choosing the Right Floating Valve for Your Water Systems
